Increasing memory allocation
The virtual users that access your web server require memory to prepare requests, send requests, and receive responses. Because the amount of memory is not automatically set on remote computers, you might receive an out-of-memory error. To correct this situation, increase the memory allocation for that computer.
About this task
If you see out-of-memory issues, it is a good practice to first check the javacore* file. You can also look at the results and verify that the server is responding correctly because many times errors can lead to excessive resource consumption. You can also monitor memory usage with Task Manager or other tools at varying user load levels such as 10, 50, 100, 500 or 1000 users and use that data to make an estimate of the memory needs per virtual user and then project memory requirements for larger user loads. In some cases the best solution is to add another agent.
- For 32-bit Java Runtime Environment (JREs), Rational® Performance Tester sets 70% of the size of physical memory to RPT_DEFAULT_MEMORY_SIZE. Typically, the maximum limit is set to 1200m.
- For 64-bit JREs, some workloads might perform better with a lesser heap size than 70% of physical memory up to a maximum of 12000m.
Procedure
To increase the memory allocation on a remote computer:
-
In the Test Navigator (from your local computer),
expand the project until you find the deployment location that you
want to change.
Deployment locations are represented by the
 icon.
icon. - Right-click the deployment location, and then click Open.
- Under Property Groups, click the General Properties link, and then click Add.
-
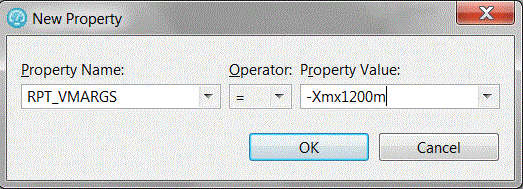
In the New Property window:If you need to set multiple RPT_VMARGS values for a location, place them in the same property entry and separate them with a space. Do not use multiple property entries to set multiple RPT_VMARGS values for a location.The following New Property window sets maximum heap to 1200 megabytes:
 Tip: It is a good practice is to monitor memory usage with Task Manager or other tools at varying user load levels such as 10, 50, 100, 500 or 1000 users and use that data to make an estimate of the memory needs per virtual user and then project memory requirements for larger user loads. In some cases the best solution is to add another agent.
Tip: It is a good practice is to monitor memory usage with Task Manager or other tools at varying user load levels such as 10, 50, 100, 500 or 1000 users and use that data to make an estimate of the memory needs per virtual user and then project memory requirements for larger user loads. In some cases the best solution is to add another agent.