Adding binary tokens
You can add binary tokens if you want authentication by using a keystore and certificate alias.
Before you begin
Note: If you did not define identity store
in Architecture School (refer to identity store), you must create
one before you create a binary token. You can create only one binary
token for each certificate alias in the keystore.
About this task
To add a binary token:
Procedure
- Open a SOAP message for editing.
- On the Config page, right-click the node and click Properties.
- In the Field Properties dialog, click the WS-Security tab.
- On the WS-Security page, ensure that the Enable field is selected.
- Select Binary Token from the list.
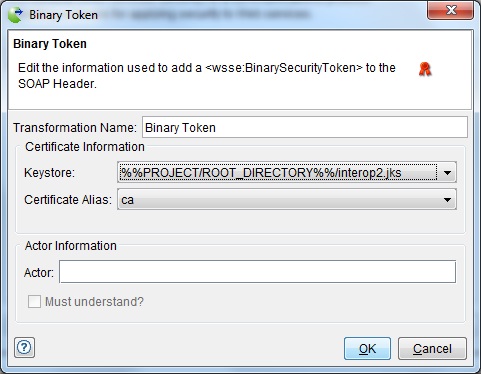
The Timestamp Token editor is displayed.
 Note: If you did not define identity store in Architecture School (refer to identity store), you must create one before you create a binary token. You can create only one binary token for each certificate alias in the keystore.
Note: If you did not define identity store in Architecture School (refer to identity store), you must create one before you create a binary token. You can create only one binary token for each certificate alias in the keystore.A binary token adds a <wsse:BinarySecurityToken> element to the SOAP header. The binary token defines a keystore ( Rational® Integration Tester Identity Store) and public key alias to authenticate the SOAP message.
- Optionally, you can define Actor/Role information
to further secure the token and the message (actor/role and mustUnderstand).
The following fields and options are part of the binary token:
Field Description Transformation Name (Required) User-defined name for the security action (helps identify the action in the main list). Keystore The Rational® Integration Tester identity store to use. Certificate Alias The public key alias to use (defined in the selected keystore). Actor Indicates a specific message receiver (either the ultimate receiver or an intermediary). For each actor/role that is defined (that is, in multiple tokens), a separate security header is added to the SOAP header. Must understand If enabled, makes the SOAP header mandatory for the specified actor/role. In this case, either the header block must be processed or the entire SOAP message must be ignored, and a SOAP fault must be generated. If not enabled, the specified actor/role may or may not process the SOAP header.